
- #Openzfs hardware requirements install#
- #Openzfs hardware requirements update#
- #Openzfs hardware requirements archive#
- #Openzfs hardware requirements full#
- #Openzfs hardware requirements software#
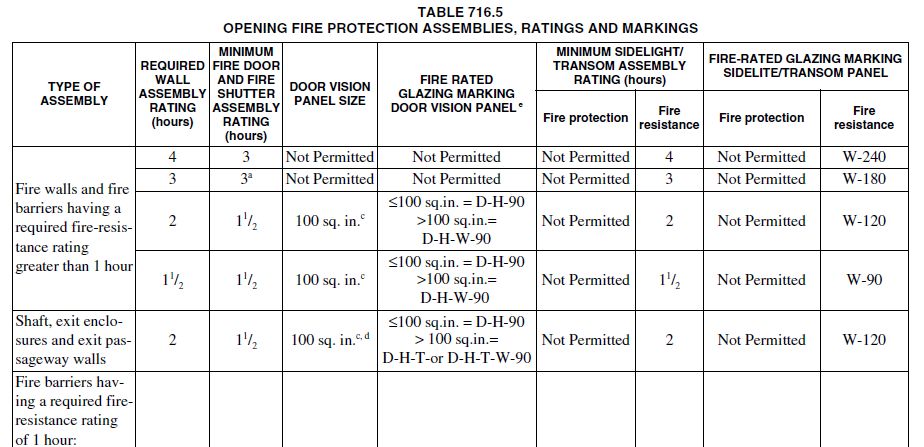
This would allow more flexible pool design to trade-off among space, redundancy and efficiency.ĭifferent configurations may have different IO characteristics under certain workload pattern, please refer to see also section at the end of this page for more information. If building a pool with a larger number of disks, you are encouraged to configure them into more than one group and finally construct a stripe pool using these vdevs. Stripe pool (similar to raid-0, no redundancy) Raidz2 pool (similar to raid-6, ≥ 4 disks, 2 disks redundancy) Raidz1 pool (similar to raid-5, ≥ 3 disks, 1 disk redundancy) Mirror pool (similar to raid-1, ≥ 2 disks, 1:1 redundancy) The most common pool configurations are mirror, raidz and raidz2, choose one from the following: These can be found in /dev/disk/by-partlabel/. When using partitions (or preparing the disk manually in advance) it is possible to also use the GPT partition labels to identify the partition/disk, as they are customizable and nicer for humans to understand. In case of using whole disks ZFS will automatically reserve 8 MiB at the end of the device, to allow for replacement and/or additional physical devices that don't have the exact same size as the other devices in the pool. These names can be retrieved with ls -l /dev/disk/by-id/ or ls -l /dev/disk/by-path/ In the world of ZFS, device names with path/id are typically used to identify a disk, because the device names like /dev/sdX may change on every start.
#Openzfs hardware requirements full#
It is recommended to use more than 1 whole disk to take advantage of full benefits, but it's fine to proceed with only one device or just a partition.

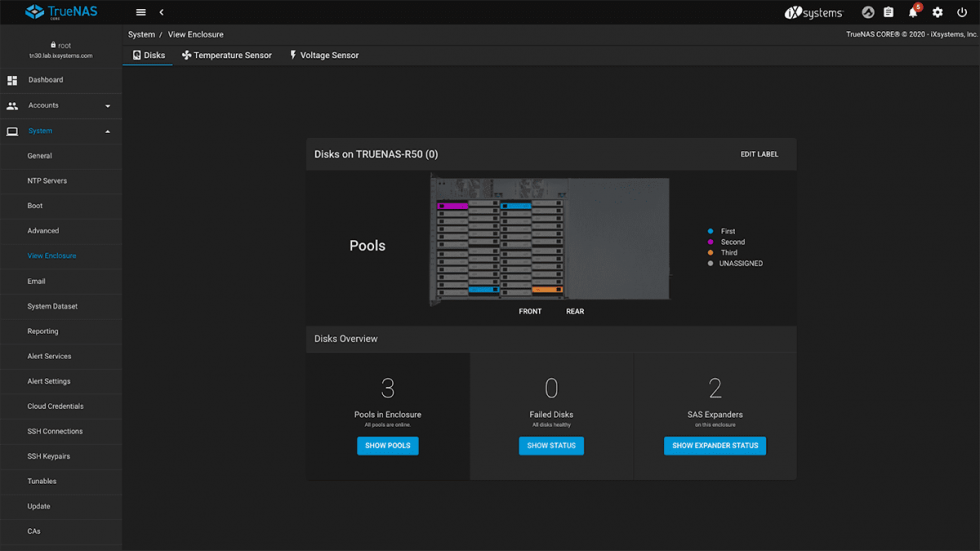
Many disks can be added to a storage pool, and ZFS can allocate space from it, so the first step of using ZFS is creating a pool.
#Openzfs hardware requirements install#
Install the linux-headers- package to always have the latest linux headers installed (analog to the linux-image- package). The modules will be built automatically only for kernels that have the corresponding linux-headers package installed. If automatic installation of Recommends is disabled it is also necessary to install zfs-dkms. Sudo apt install linux-headers-amd64 sudo apt install -t bullseye-backports zfsutils-linux Make sure /etc/apt/sources.list contains correct Debian codename backports:Ĭodename=$(lsb_release -cs) echo "deb $codename-backports main contrib non-free"|sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list & sudo apt updateĪnd on DebianBullseye you may then install it using: If You have received following notice in return:Į: The value 'buster-backports' is invalid for APT::Default-Release as such a release is not available in the sources" Sudo apt install -t buster-backports zfsutils-linuxįuture updates will be taken care by apt.
#Openzfs hardware requirements update#
When configured, use following commands to install the packages: sudo apt update Upstream stable patches will be tracked and compatibility is always maintained. Also, it is recommended by Debian ZFS on Linux Team to install ZFS related packages from Backports archive. It is necessary to add the contrib section to your apt sources configuration to be able to get the packages. ZFS on Linux is provided in the form of DKMS source for Debian users.
#Openzfs hardware requirements software#
This page will demonstrate using ZFS on Linux (ZoL) if not specifically pointed to the kFreeBSD or FUSE implementation.ĭue to potential legal incompatibilities between the CDDL and GPL, despite both being OSI-approved free software licenses which comply with DFSG, ZFS development is not supported by the Linux kernel. There is also a deprecated userspace implementation facilitating the FUSE framework.
#Openzfs hardware requirements archive#
Debian kFreeBSD users are able to use ZFS since the release of Squeeze, for those who use Linux kernel it is available from contrib archive area with the form of DKMS source since the release of Stretch.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
